
Cybersecurity
Cybersecurity is the practice of protecting systems, networks, and data from digital attacks, unauthorized access, and damage. As technology advances, the need for robust cybersecurity has become crucial, with threats like data breaches, ransomware, and phishing evolving rapidly. In 2024, cybersecurity focuses on advanced solutions like AI-powered defenses, zero trust models, and increased cloud security, ensuring that individuals, businesses, and governments can safeguard sensitive information in an increasingly connected world. https://gsconlinepress.com/journals/gscarr/sites/default/files/GSCARR-2024-0211.pdf
Cybersecurity in 2024
As technology rapidly evolves, so does the complexity of cyber threats, making cybersecurity a critical concern in 2024. The increasing digitization of industries, the proliferation of connected devices, and the rise of remote work have expanded the cyber-attack surface, leaving individuals, businesses, and governments vulnerable to sophisticated attacks. This detailed overview explores key areas shaping cybersecurity in 2024, from emerging threats and technologies to best practices for safeguarding digital assets.

1. The Growing Threat Landscape
In 2024, cybercriminals are using more advanced tools and techniques to launch increasingly sophisticated attacks. Ransomware, phishing, and supply chain attacks are among the top threats, affecting industries ranging from healthcare and finance to critical infrastructure.
-
Ransomware
Ransomware has become more dangerous, with cybercriminals not only demanding ransoms for encrypted data but also threatening to release sensitive information if payments aren’t made.
-
Phishing
It continues to evolve with highly targeted, AI-driven spear-phishing campaigns, making it harder for even the most vigilant users to detect fraudulent emails.
Supply Chain Attacks
are becoming more common, as attackers exploit third-party vendors or service providers to infiltrate larger targets, resulting in widespread damage.
Key Statistics for 2024:
- Global cybercrime damages are projected to reach $10.5 trillion annually by 2025.
- Over 50% of ransomware victims pay the ransom, though only a fraction successfully recovers all their data.
2. The Role of Artificial Intelligence in Cybersecurity
Artificial intelligence (AI) is playing an increasingly important role in both the offense and defense of cybersecurity. AI-powered cyberattacks use machine learning algorithms to adapt to defensive measures and find vulnerabilities in real time. On the defensive side, AI is being leveraged to detect anomalies, analyze vast amounts of data, and predict potential threats before they occur.
-
AI Driven Attacks
Cybercriminals are using AI to automate and scale attacks, making them more effective and harder to defend against.
-
AI for Defense
AI helps cybersecurity professionals identify threats faster, mitigate risks, and improve overall system resilience by detecting patterns and anomalies that human analysts might miss.
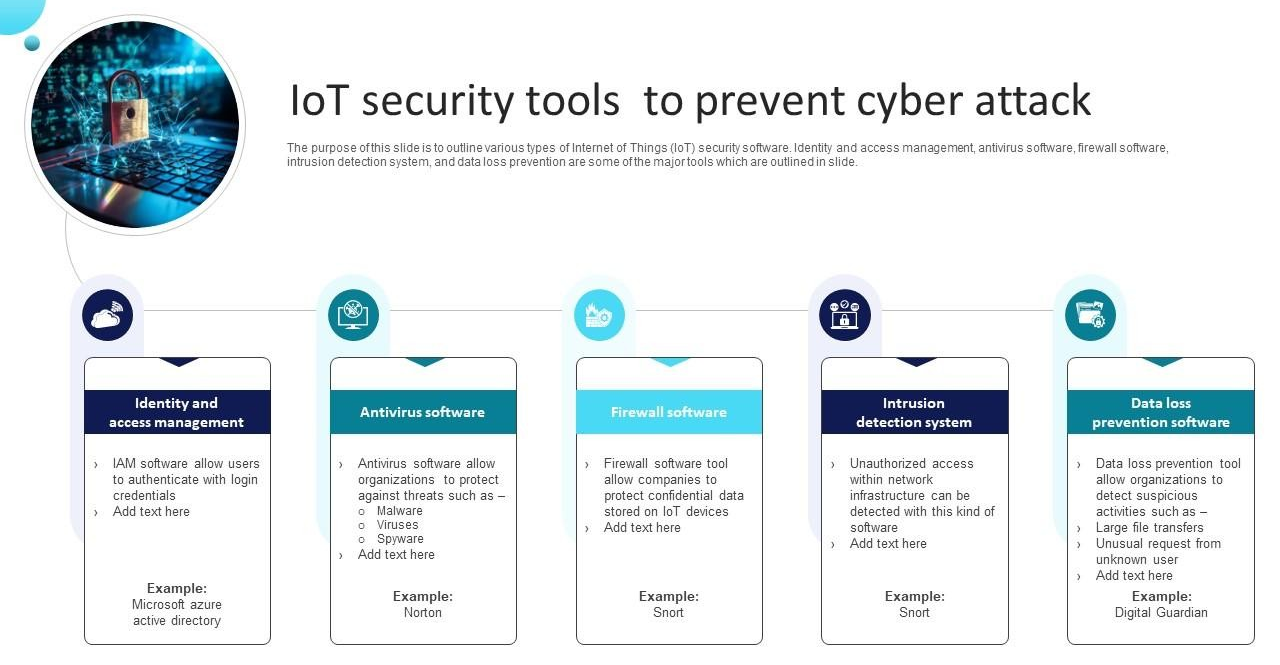
3. Rise of IoT and Connected Devices
The Internet of Things (IoT) has significantly expanded the cyber-attack surface. In 2024, there are billions of connected devices, from smart home gadgets to industrial machinery, that often lack robust security features, making them prime targets for attackers.
-
IOT Vulnerabilities
Many IoT devices are not designed with security in mind, with weak encryption and outdated firmware, leaving them open to exploitation.
-
Botnets
Hackers can take control of insecure IoT devices and use them to create botnets that launch Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) attacks, which can cripple websites or networks.
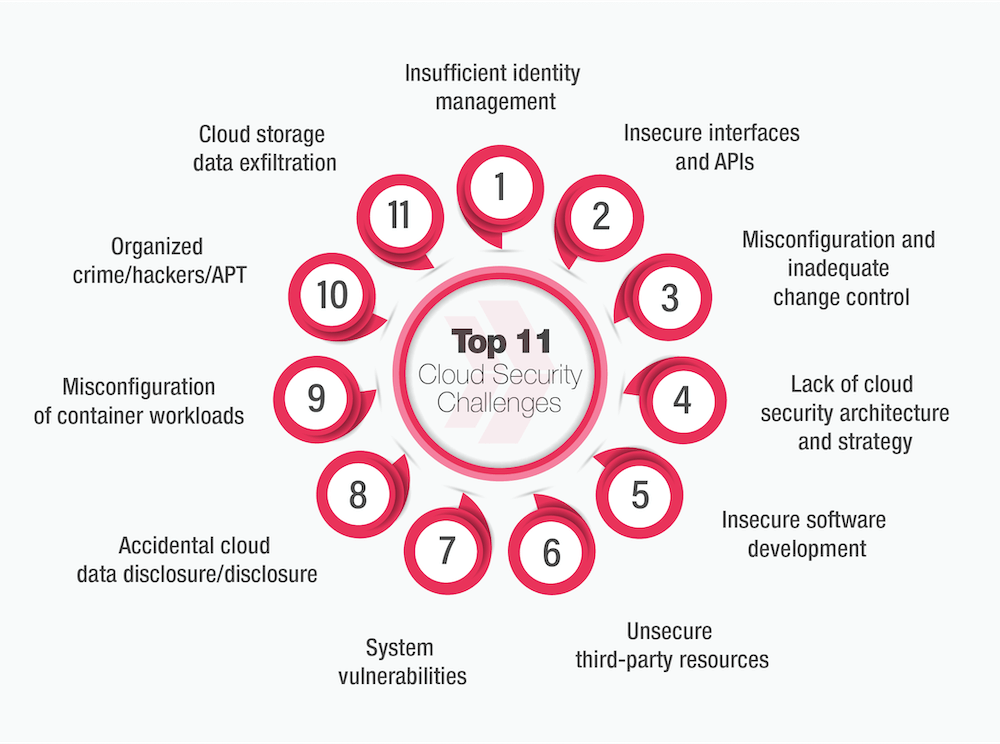
4. Cloud Security Challenges
With the widespread adoption of cloud services, ensuring the security of data stored and processed in the cloud is a major concern. Cloud misconfigurations, insufficient access controls, and shared responsibility models between cloud providers and clients can lead to security breaches.
-
Misconfigurations
One of the leading causes of cloud data breaches in 2024 is simple human error, where cloud environments are improperly configured, leaving sensitive data exposed.
-
Zero Trust Architecture
To combat cloud security challenges, organizations are adopting a “zero trust” security model, which assumes no user or system should be trusted by default and requires continuous verification.
5. The Impact of Remote Work on Cybersecurity
The post-pandemic shift to remote work has created new cybersecurity challenges. In 2024, many employees continue to work from home, using personal devices and unsecured networks to access corporate resources, increasing the risk of cyberattacks.
-
Home Network Vulnerabilities
Employees accessing sensitive company data from unprotected home networks make organizations more vulnerable to attacks.
-
Increased Phishing
Cybercriminals exploit remote work conditions through phishing campaigns, taking advantage of the less secure environments to steal credentials.
6. Nation-State Cybersecurity Threats
Nation-state cyberattacks have become more frequent and damaging in 2024. These attacks are highly targeted, focusing on critical infrastructure, government agencies, and high-value businesses.
-
Espionage
Nation-state attackers are often motivated by political or economic gain, engaging in cyber espionage to steal intellectual property or sensitive government data.
-
Cybersecurity Warfare
Some nation-states use cyberattacks as a tool for sabotage, disrupting the operations of rival nations or companies to cause chaos and damage.
7. Regulatory Changes and Compliance
In response to the growing threat of cyberattacks, governments and regulatory bodies have introduced stricter regulations and compliance standards for data protection and cybersecurity. Organizations in 2024 must comply with frameworks such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR), the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA), and others.
-
GDPR
Europe’s GDPR continues to enforce strict penalties on companies that fail to protect user data, encouraging businesses to adopt more rigorous security measures.
-
Global Regulations
Other regions, including the U.S., are introducing new laws focused on data protection, cybersecurity standards, and consumer privacy.
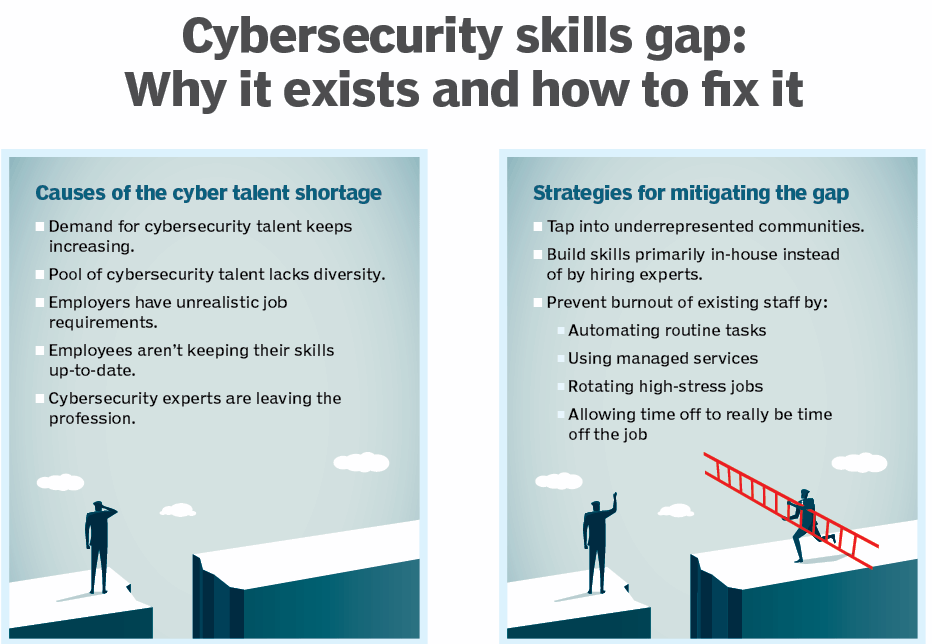
8. Cybersecurity Skills Gap
Despite the growing importance of cybersecurity, there remains a significant talent shortage in the field. In 2024, organizations are struggling to find qualified cybersecurity professionals, which leaves them vulnerable to attacks.
-
Skills Gap
With a global shortage of 3.5 million cybersecurity professionals, companies are adopting automation and AI solutions to address the gap.
-
Training Initiatives
Organizations are increasingly investing in upskilling their workforce, while also providing comprehensive training for employees in cybersecurity awareness. By doing so, they aim to significantly reduce insider threats and continuously improve their overall security posture.
Read more Articles Here, Read Previous Also